- Cryptocurrency
- March 19, 2025
Table of Contents
Online scams are becoming more sophisticated, and one of the latest threats is crypto blackmail scams. Scammers send emails claiming they have compromising videos or personal information, demanding a Bitcoin payment to avoid exposure.
This alarming new email extortion scheme has targeted thousands, especially Gmail users, through sextortion email scams. These frauds lead to psychological distress with victims concerned with their information being revealed. These frauds also make one feel cornered since the scammers keep asking for money even after receiving payment.
In this guide, we’ll break down what these scams are, how to recognize them, real-world examples of crypto scams and Bitcoin scams, and what to do if you receive a threatening email asking for Bitcoin.
What Are Blackmail Scams?
A blackmail scam is a type of cyber fraud where scammers threaten to release sensitive or embarrassing information unless the victim pays them money—often in Bitcoin. These scams typically appear in email scams, texts, or even phone calls.
There are different types of online blackmail scams, including:
- Bitcoin Sextortion Scam: Scammers claim to have explicit recordings of you
- Video Blackmail: Threats to leak personal videos.
- Extortion Email Scams: Fraudulent messages demanding payment under threats.
Many victims panic and pay the ransom, but these threats are often false. Unlike legitimate businesses or debt collectors, blackmailers often demand payment in cryptocurrency (like Bitcoin) because it is harder to trace.
This is a hallmark of any crypto scam—scammers exploit the anonymity of blockchain transactions to hide their tracks.
What is Crypto Blackmail Scam?
A new Email Extortion Scheme is circulating, often referred to as a Bitcoin Sextortion Scam. Scammers claim they have hacked into your device and recorded you via your webcam. They demand Bitcoin to prevent them from sharing embarrassing or private footage.
In reality, the scammer may not have any real information at all. They rely on fear to pressure you into paying quickly. This type of crypto blackmail scam is widespread because:
- Bitcoin Scams Demand Cryptocurrency: Transactions are irreversible
- Impersonating Tech Experts: They claim they have specialized “hacking” skills to gain credibility.
- Sense of urgency: They’ll threaten to release the alleged content if you don’t comply immediately.
Did You Receive a "Threatening Email Asking for Bitcoin?"

If you get a sextortion email saying, “I have a recording of you” or “Send Bitcoin, or I will release your secrets,” don’t panic. These are fraudulent extortion emails designed to manipulate you. Knowing how to tell if a sextortion email is real can save you from panic.
Red Flags of a Bitcoin Scam Email:
- Grammatical Errors: Real hackers or extortionists aren’t always perfect, but obvious typos suggest a mass mailing.
- Generic Subject Lines: Titles like “Important Info” or “I Have Evidence” appear in countless blackmail email scams.
- Unverifiable Proof: They might claim they hacked your camera, but they seldom provide any authentic screenshots or undeniable evidence.
Before you fall for a Bitcoin scam email, take a breath. Many of these messages are designed to scare you into paying before you can think logically.
Should you Ignore Extortion or Threatening Emails?
If you have solid reasons to believe the threat is not real—like no actual personal details are shown or the scammer’s claims are overly generic—it’s often best not to engage. However, someone blackmailing you is serious business, and you should:
- Keep Evidence: Don’t delete the email; save it in a secure folder.
- Report It: Notify local law enforcement or file a complaint with the FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3).
- Protect Yourself: Change passwords and enable multi-factor authentication on key accounts—particularly your Gmail if it’s a blackmail scam targeting Gmail users.
How to Spot Online Scams Through Emails, Text Messages, or Calls?
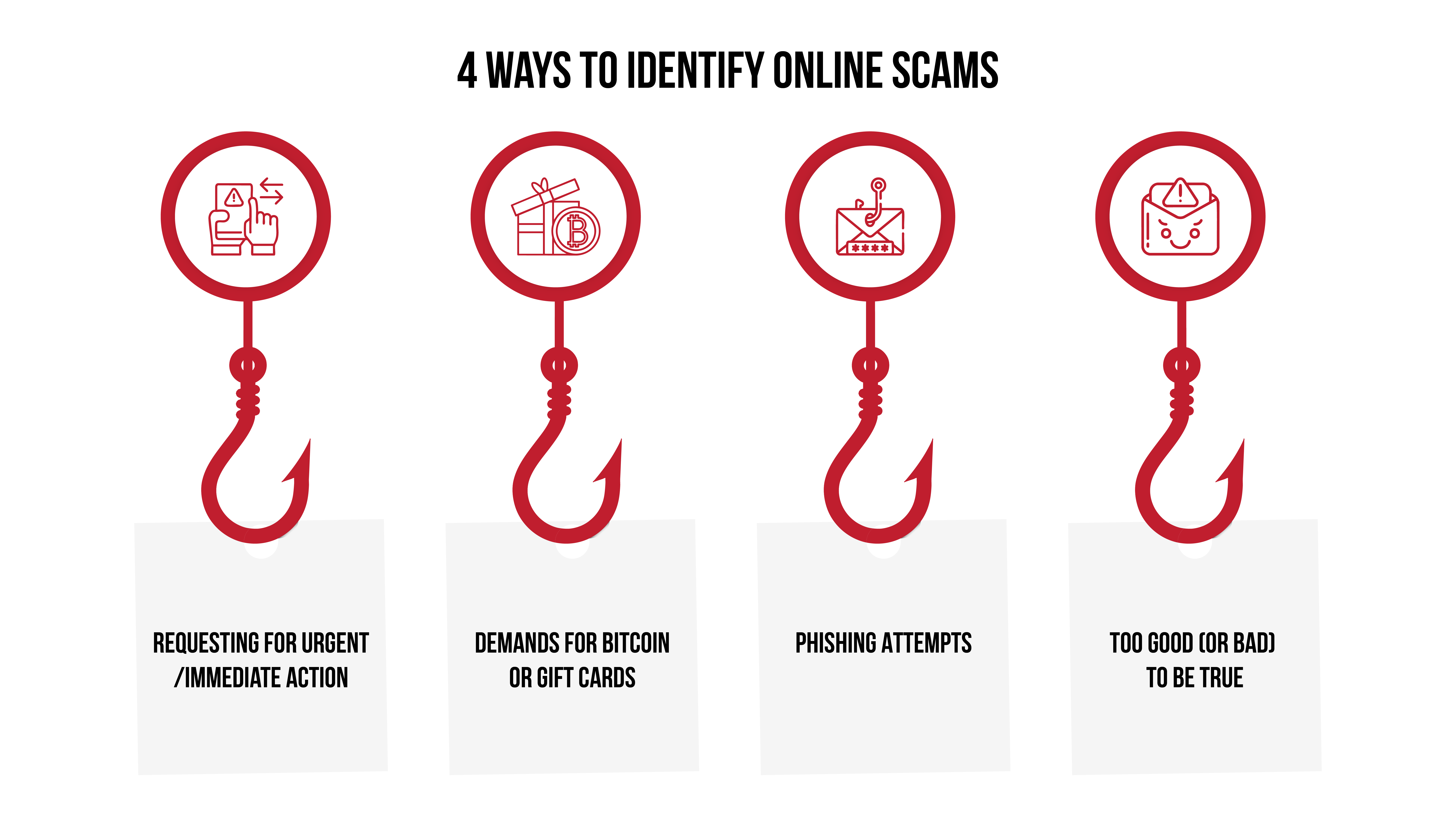
Cybercriminals use every possible channel to launch their online extortion attempts. Whether through emails, texts, or even phone calls, here’s what to look for:
- Requests for Urgent Action: “Pay now or else…”
- Demands for Bitcoin or gift cards: Hallmarks of a Bitcoin scam or advanced fee scam.
- Phishing Attempts: Messages prompting you to click suspicious links or download attachments.
- Too Good (or Bad) to Be True: Overly threatening or overly enticing messages are usually red flags.
Crypto Blackmail Scams: How to Spot & Avoid Them
Crypto/Online Blackmail Scams can be terrifying if you’re unprepared. Here’s how you can protect yourself:
1. Strengthen Account Security
- Use unique, strong passwords and a password manager.
- Enabletwo-factor authentication (2FA) to protect against hackers.
2. Verify Sources
- Double-check email addresses. Cybercriminalstendto utilize addresses that arenearly legitimate but containslightmisspellings.
- Never download attachments if you are notsure of the sender's identity.
3. Stay Informed on New Tactics
- Dark web cybercriminals are always coming up with new tactics.
- Follow trusted cybersecurity blogs and law enforcement agency alerts.
4. Contact Authorities
- If you’re dealing with an actual threat, immediately contact local law enforcement or specialized cybercrime units.
How Extortion Emails Look Like?
Extortion emails typically have these characteristics:
- Subject Line: “Your Webcam Was Hacked” or “I Recorded You.”
- Threat: They claim to have access to your browsing history or recorded footage.
- Demand: They often provide a cryptocurrency wallet address where you must send money immediately.
- Deadline: “Send [X amount] in 24 hours, or I’ll share this with all your contacts.”
Example of a Common Blackmail Email Scam:
Subject: URGENT: I Have A Video Of You
I hacked your webcam while you were on an adult website. I recorded everything and will send the video to your contacts unless you send $1,200 in Bitcoin to the wallet address below within 48 hours.
Real-World Example: The Pegasus Email Scam
A rising blackmail email scam involves Pegasus spyware—a tool used by governments for surveillance but now falsely claimed by scammers to have hacked your device.
Victims receive threatening emails asking for Bitcoin, alleging Pegasus was used to access their webcam and personal data. The scammer demands a cryptocurrency ransom to prevent supposed leaks.
How to Spot the Pegasus Scam Email:
- Claims your device is hacked with Pegasus spyware
- Threatens to leak private videos or data unless Bitcoin is paid
- Includes personal details (passwords, addresses) to seem credible
Conclusion
With the current digital era, crypto blackmail scams have evolved to be more advanced, tricking unsuspecting victims with blackmail email scams, Bitcoin scam emails, and sextortion threats.
These online scams usually employ tactics of fear, threatening to extort Bitcoin payments under false conditions. The most important aspect of avoiding online blackmail scams, however, is awareness and prevention.
- Stay Calm & Check: Look for actual proof; do not hurry to pay.
- Enhance Security: Change passwords and implement two-factor authentication.
- Report & Block: Alert law enforcement and block suspicious senders.
Need help to recover funds lost to a scam? Global Financial Recovery specializes in helping victims fight back against online blackmail fraud and crypto scams. Don’t let scammers win—take control today.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Sextortion is online blackmail where scammers threaten to leak intimate images or videos unless you pay. They often lure victims via social media or dating apps.
Report it to the platform immediately. Many laws protect against image-based abuse, and authorities can help get content removed.
Yes! Many extortionists use fake legal notices or claim they are from government agencies. Never respond—verify with official sources first.
- Extortion is generally defined as blackmail threats that require payment of money or other favors usually masked in threats.
- Sextortion is a form of extortion where the blackmailers threaten to post the most personal private photos or videos of the individual to blackmail them.
Scammers send mass emails using leaked email lists from data breaches, hoping someone falls for their threats.





