- Cryptocurrency
- April 22, 2025
Table of Contents
Fake tax scam emails and crypto phishing scams have become increasingly common. Scammers use these methods to trick unsuspecting victims into paying fake taxes or sharing sensitive personal information. This often leads to massive financial losses. Tax refund fraud and IRS phishing scams have become significant threats to crypto investors.
Moreover, the IRS has warned that these scams have led to major financial losses as scammers steal crypto through fake tax demands. This growing threat erodes trust in crypto investments.
This article will break down how these scams work, red flags to look for, real-world cases, and how you can protect yourself from falling victim.
What is a Fake Crypto Tax Scam Email?
The fake tax scam email presents itself as communication from a real tax organization to trick victims into believing their crypto investments require tax payments. The emails display official-looking tax agency elements such as logos and addresses. Such malicious emails represent intentional attempts to obtain both your funds and personal information.
Crypto Phishing Scams
In a crypto phishing scam, fraudsters often impersonate agencies like the IRS, claiming that the victim owes back taxes on their cryptocurrency. They might ask for immediate payments or offer a “tax refund,” only to steal the funds once paid.
- Fake Crypto Tax Refund Scam: The scammer may promise a tax refund in exchange for your personal information or funds.
- Tax Payment Demands: False accusations of unpaid crypto taxes
How Scammers Use Phishing Emails to Steal Crypto?
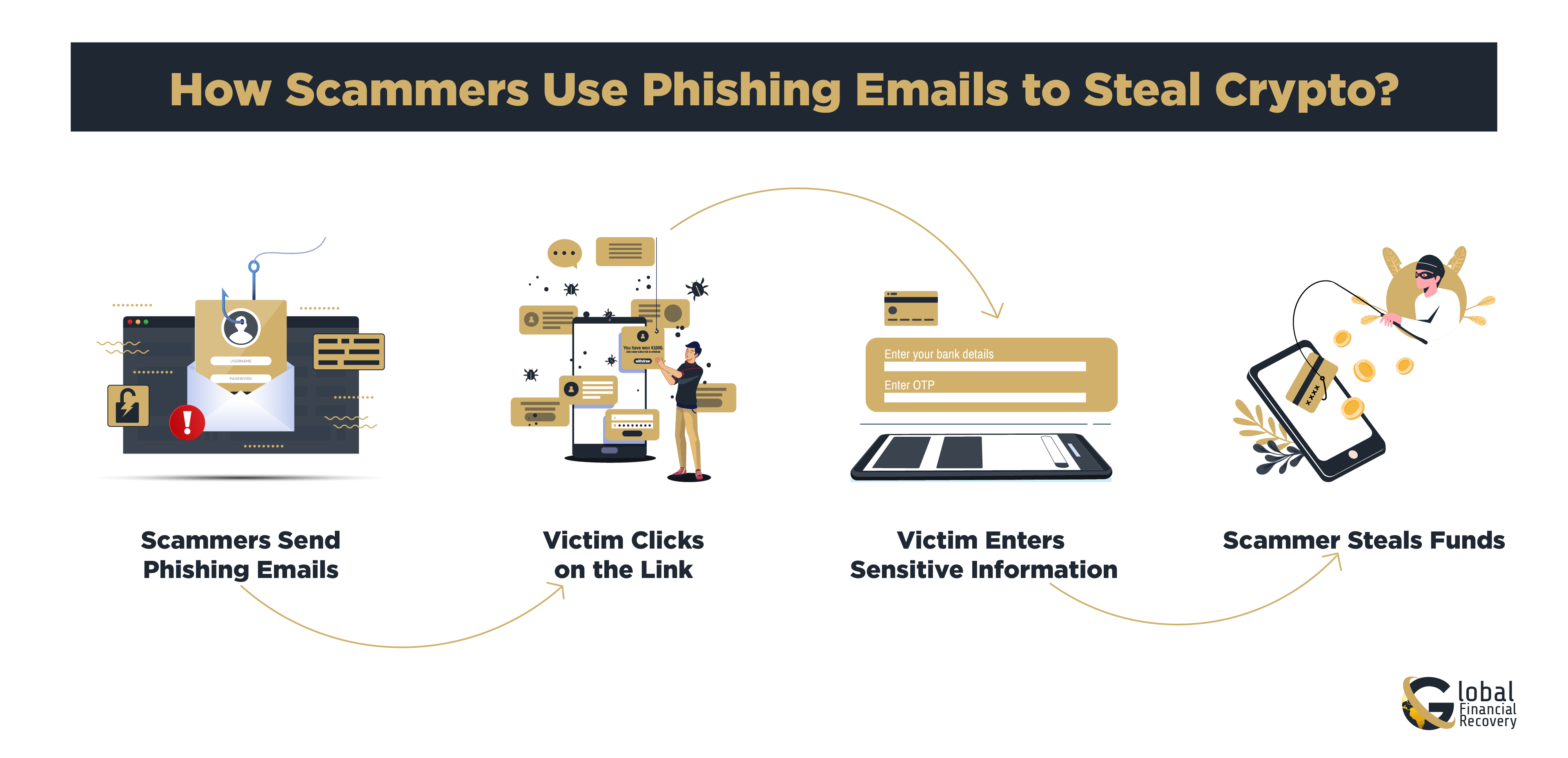
Phishing emails are one of the most common tactics used by scammers to steal cryptocurrency. Here’s how it typically works:
- Scammers Send Phishing Emails: The IRS and other government agencies might be displayed in such a way to convince victims that the email is real, and so they look real, with logos, official-looking text, and links that also seem real.
- Victim Clicks on the Link: The email comprises a link that leads the victim to a fake website that very closely resembles the real site of a government agency or crypto exchange.
- Victim Enters Sensitive Information: Once on the fake site, the victim is required to give some personal information, such as passwords, Social Security numbers, or some private keys of crypto wallets.
- Scammer Steals Funds: The impostors then go ahead and steal by using the same information to withdraw funds directly from the victim's account or crypto wallet.
Common Phishing Methods Used by Scammers
These scams often involve fraudulent communication that appears to come from trusted sources such as tax authorities, financial institutions, or crypto exchanges. Here's how scammers use phishing methods to steal crypto from unsuspecting victims.
1. Impersonating IRS Tax Agents and Requesting Crypto Payments for Supposed Back Taxes
Scammers who utilize phishing scams often act like they are impersonating IRS tax agents or government authorities to scare victims into believing they owe fake taxes for their cryptocurrency trading activity. This strategy takes advantage of urgency and fear to compel victims into action before considering the legitimacy of their demand
How It Works:
- The scammer sends an email (text) to the victim stating that they owe taxes or fines related to their cryptocurrency trades.
- The scam message has a fake IRS logo that looks authentic and tells the victim that they must pay the taxes immediately or they will face legal action, and assets could be frozen.
- The victim receives a link (or phone number) to pay off the issue, which is a phishing site designed to gain access to their personal and financial information.
2. Fake Tax Refund Offers That Seem Too Good to Be True
Some fraudsters will pretend to offer tax refunds as a lure for victims to provide personal information or make cryptocurrency payments. The scam sends a phishing email claiming a sizable tax refund based on the recipient's holdings of crypto assets. Typically, the scam displays a notice that the victim is owed a refund based on overpaid taxes.
How It Works:
- Fraudsters email the victim and claim that they are owed a "tax refund" based on crypto transactions.
- Receivers of the email are asked to provide personal information, click on a link to fill out a request form, or possibly pay a small "processing fee" using cryptocurrency.
- If this request and payment are initiated or information is provided, the fraudster then utilizes the information for theft of consumer funds or identity theft.
3. Mimicking Trusted Crypto Platforms (Coinbase, Binance, etc.) to Steal Login Details
Phishing scams targeting crypto investors often impersonate popular exchanges like Coinbase or Binance to steal login credentials and access wallets. These phishing attempts are designed to look exactly like the login pages of trusted crypto platforms.
How It Works:
- Victims aresent fake emails or SMS notificationsstating there isaproblem with their account (e.g., suspicious activity).
- The scam message contains a link to animitation login page that istheexactreplica of the original exchange.
- The victim inputs their login credentials, and the attacker uses them to withdrawmoney from their account.
4. Phishing Attacks Using Fake Tax Forms and Documents
The fraudsters will send forged tax documents that look like legitimate tax documents (e.g., W-9, 1099) to deceive victims into disclosing personal information. These documents frequently indicate that the victim owes taxes on their cryptocurrency or that they must submit it to avoid penalties
How It Works:
- The fraudster sends an email with a forged tax document asserting that the victim owes taxes on their crypto assets.
- The victim is instructed to open the form and provide more personal information, or their cryptocurrency will be frozen.
- The form might contain sensitive information, such as Social Security numbers and wallet keys, or his account information for the crypto exchange.
5. SMS Phishing (Smishing) Using Fake Tax Claims
Smishing, or SMS phishing, occurs when scammers send fraudulent tax claims via text message. These messages often create a sense of urgency, making the victim believe they need to act immediately to avoid legal issues or crypto account seizures.
How It Works:
- Targets receive a message informing them of the taxes due on their cryptocurrency earnings and have to act soon before facing any issues or getting shut down.
- The link sent is that of a mock website that collects people's info or money.
- Once details are entered on the imitation site, the scammer steals crypto or personal information.
How Scammers Use Government Logos to Enhance Credibility?
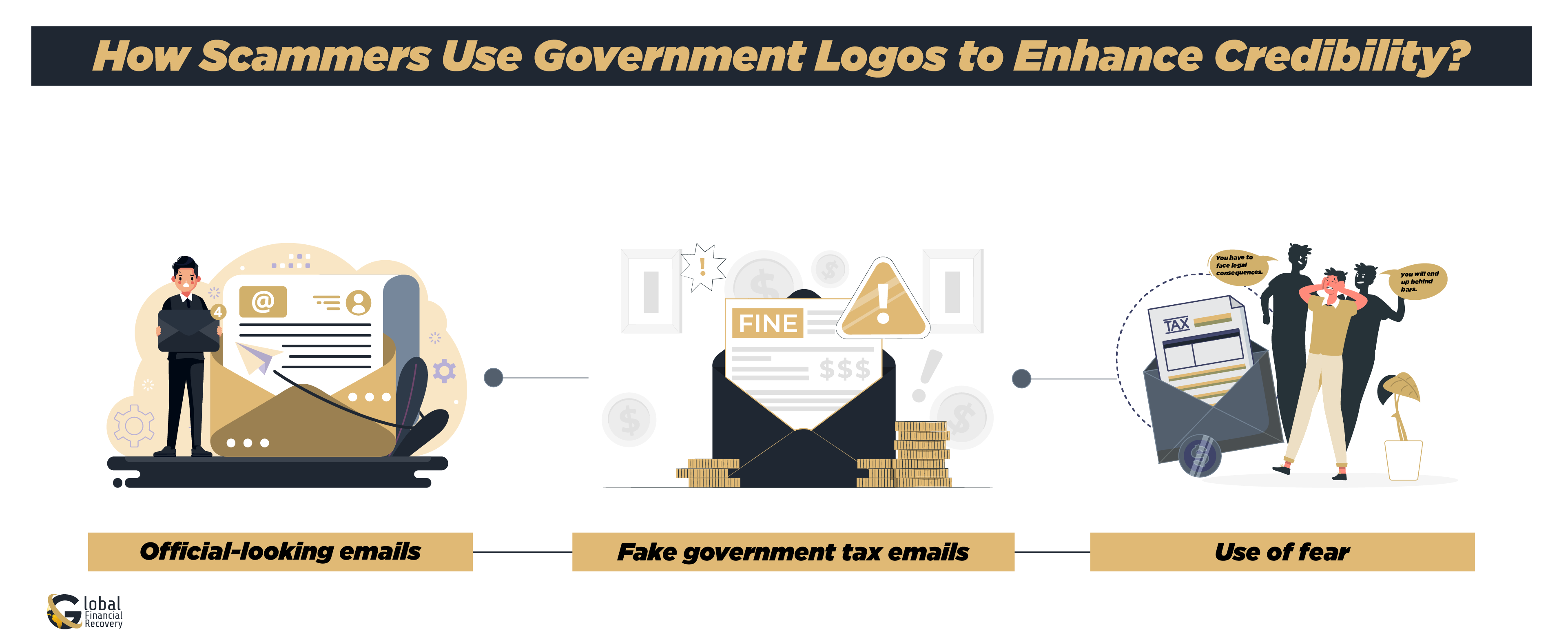
Crypto phishing scams usually employ government logos to present the emails as legitimate. Scammers impersonate government agencies such as the IRS by replicating their logos and wording to give the email an official appearance. This is how this trick works:
- Official-looking emails: Spammers send emails with government logos and bogus tax refund notices.
- Fake tax emails from the government: Such emails may appear so real that victims rarely resist clicking on the link or paying the amount requested.
- Use of threat: To rush the victim into acting, such emails tend to threaten legal proceedings or asset seizures.
By employing formally branded materials, the fraud appears more authentic, and the scammer has a better chance of succeeding in deceiving the victim.
Red Flags of Fake Tax Emails & Phishing Scams
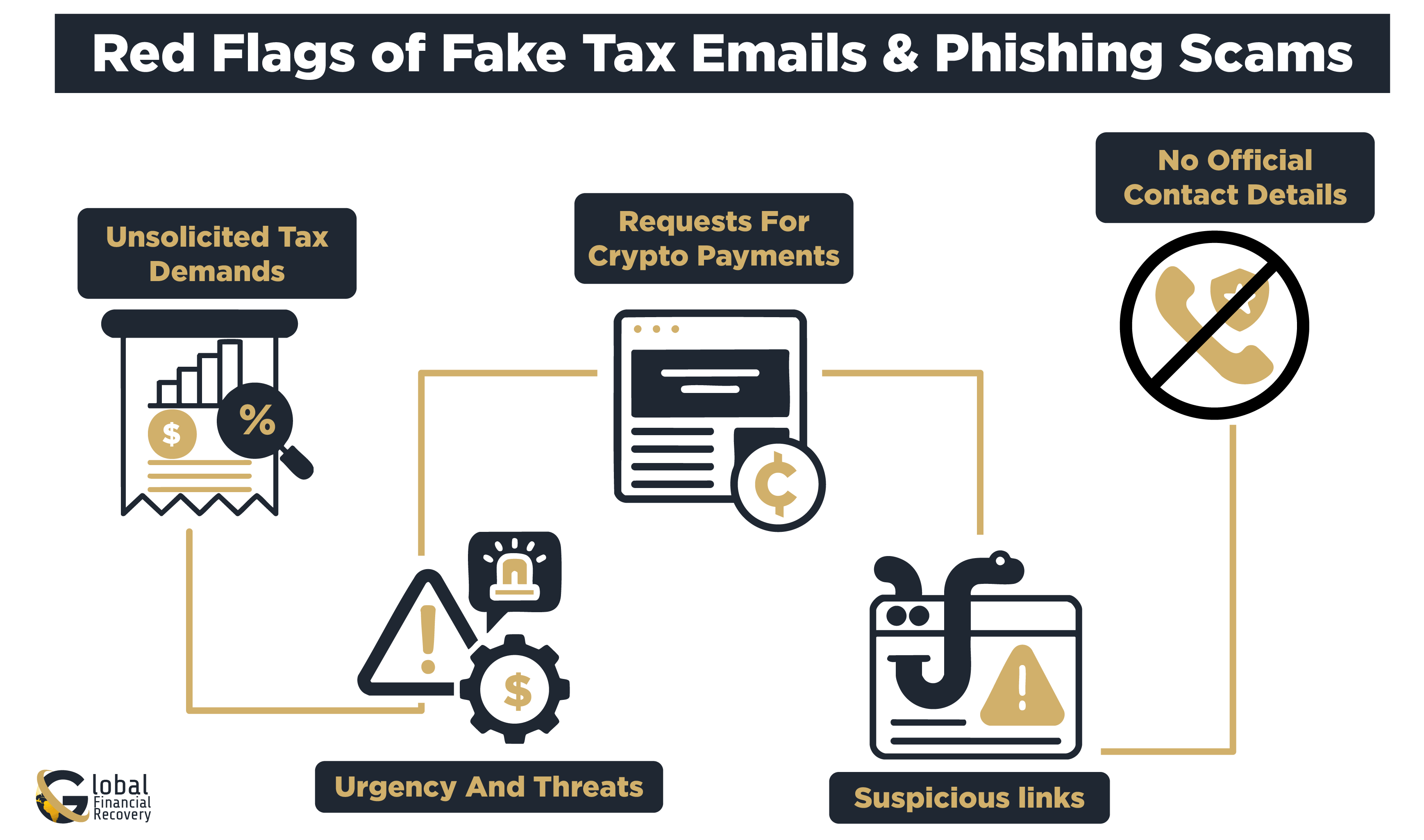
Recognizing fake tax scam emails is crucial for protecting your crypto assets. Look out for the following red flags:
- Unsolicited tax demands: If you get an unexpected email from the IRS or any tax authority, always check the source before responding.
- Urgency and threats: Scammers tend to make you feel a sense of urgency by threatening to take legal action if you do not comply immediately.
- Requests for crypto payments: No legitimate tax authorities accept cryptocurrency for tax payments.
- Suspicious links: Hover over any links in the email to determine if the website URL appears genuine. If it is misspelled or has an unusual domain, it is a warning sign.
- No official contact details: Emails that fail to include official contact details should be viewed as suspicious.
To learn about it in detail, read How Scammers Trick Crypto Investors with Fake Tax Demands?
Examples of Fake Tax Phishing Scams
Case: Ghost Preparers Exploiting Crypto Tax Filings
The tax preparer Emily employed offered large tax refund possibilities for her cryptocurrency assets. A ghost preparer handled her tax files yet failed to submit either their signature or Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN). Emily received IRS penalties along with an audit after she submitted her taxes because the returned information contained incorrect details. The IRS warns people to stay vigilant about ghost preparers since these tax specialists improperly use crypto tax reporting intricacies to their benefit.
For more real-life cases of crypto tax scams and how victims have recovered stolen funds, visit Crypto Tax Scam Case Studies.
How to Protect Yourself from Fake Tax Notices & Phishing Attacks?
Phishing emails and fake tax notices are two of the most common techniques used by scammers to steal your personal information and funds, mostly in the world of cryptocurrencies. Follow these steps to protect yourself and your assets from conspiracy scams. While these suggestions are simple, they can be effective.
1. Verify the Legitimacy of the Tax Notice
To ensure that a tax notice is genuine, always follow these verification steps:
- Contact Official Tax Authorities: Always reach out directly to the IRS or your country’s tax agency using verified contact information from their official website. This is the most reliable way to confirm whether a tax demand is legitimate.
- Check the Sender’s Email Address: Be cautious when you receive emails claiming to be from the IRS or other tax authorities. Check the sender’s email address carefully. Official emails will come from government domains, such as ".gov". Be especially cautious of slight variations or suspicious domains like ".com" or ".org".
- Look for Official Channels: Real tax authorities, like the IRS, will never ask for payment through cryptocurrency. If a tax notice demands crypto payments, this is a major red flag. Always verify such claims with the official channels directly.
2. Protect Your Crypto Assets from Phishing Scams
Crypto phishing scams are designed to steal your personal and financial information. Here’s how you can protect yourself:
- Never Send Crypto for Tax Purposes: Legitimate taxation authorities do not need cryptocurrencies to compensate for taxes. So be extremely careful when you find a request for crypto payment; that is a very firm indication that you're dealing with a scam.
- Utilizing 2FA: Activate 2-factor authentication for all the crypto platform and wallet accounts, and also secure your account using extremely secure access that renders unauthorized individuals unable to gain access even when they possess the login credentials.
- Verify official communications: Phishing attacks typically have a sense of urgency, in which alarming text is used to intimidate victims into acting hastily. Always carefully double-validate the authenticity of official communications, particularly those seeking sensitive data or instant payment.
Taking all these measures at the beginning makes you substantially avoids being scammed by imitating tax notifications, phishing emails, and other cheating tactics for attacking crypto investors.
What to Do If You’ve Fallen Victim to a Fake Tax Email Scam?

If you believe you’ve fallen victim to a crypto phishing scam or fake tax email scam, follow these recovery steps:
- Stop all transactions: Contact your crypto exchange or wallet provider immediately to block further withdrawals.
- Report the scam: Notify the IRS or relevant tax authority, as well as your financial institution.
- Seek professional recovery services: Get help from crypto fraud recovery experts to track stolen funds.
Conclusion
The rise of crypto phishing scams is alarming, but by staying informed and following best security practices, you can protect your investments. Always be skeptical of unsolicited communications, verify tax demands with official sources, and remain vigilant to avoid falling for fake tax scam emails.
Need Help Recovering Stolen Crypto?
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Spear-phishing emails are extremely targeted phishing scams, tailored with unique information about you to appear authentic. Scammers may use your actual crypto transactions to try to trick you into giving away sensitive information or making cryptocurrency payments. Always check independently with official IRS contacts.
A ghost preparer is an unethical tax preparer who charges for tax return services but will not sign the return or put their Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN) on the return as required by law. Ghost preparers often misrepresent information on a return to receive a larger refund, request cash payments, and may direct refunds to their bank accounts. A ghost preparer makes taxpayers subject to possible penalties and audits.
Smishing is a phishing method that steals sensitive data and fraudulent payments through fake SMS text messages. Scammers use text messages to pretend to be IRS agents or other tax authorities who create false claims about cryptocurrency tax issues to force victims into acting right away.
This type of scam promises easy returns and/or tax reimbursements to lure victims. To be especially careful, the IRS cautions against scams offering “crypto tax refunds,” with the sole purpose being to acquire your wallet keys or personal data.
Scammers utilize advanced AI chatbots to impersonate IRS representatives, making truly authentic conversations. They tend to push crypto investors to pay fake fees or taxes. Always confirm through official IRS channels since genuine agents will not reach you via chat platforms or social media.





